






































Prepara tus exámenes y mejora tus resultados gracias a la gran cantidad de recursos disponibles en Docsity

Gana puntos ayudando a otros estudiantes o consíguelos activando un Plan Premium


Prepara tus exámenes
Prepara tus exámenes y mejora tus resultados gracias a la gran cantidad de recursos disponibles en Docsity
Prepara tus exámenes con los documentos que comparten otros estudiantes como tú en Docsity
Los mejores documentos en venta realizados por estudiantes que han terminado sus estudios
Estudia con lecciones y exámenes resueltos basados en los programas académicos de las mejores universidades
Responde a preguntas de exámenes reales y pon a prueba tu preparación

Consigue puntos base para descargar
Gana puntos ayudando a otros estudiantes o consíguelos activando un Plan Premium
Comunidad
Pide ayuda a la comunidad y resuelve tus dudas de estudio
Descubre las mejores universidades de tu país según los usuarios de Docsity
Ebooks gratuitos
Descarga nuestras guías gratuitas sobre técnicas de estudio, métodos para controlar la ansiedad y consejos para la tesis preparadas por los tutores de Docsity
documentos importantes norma isa 5.1
Tipo: Traducciones
1 / 46

Esta página no es visible en la vista previa
¡No te pierdas las partes importantes!







































Copyright International Society of Automation Provided by IHS under license with ISA
Copyright International Society of Automation Provided by IHS under license with ISA
Copyright International Society of Automation Provided by IHS under license with ISA
Copyright International Society of Automation Provided by IHS under license with ISA
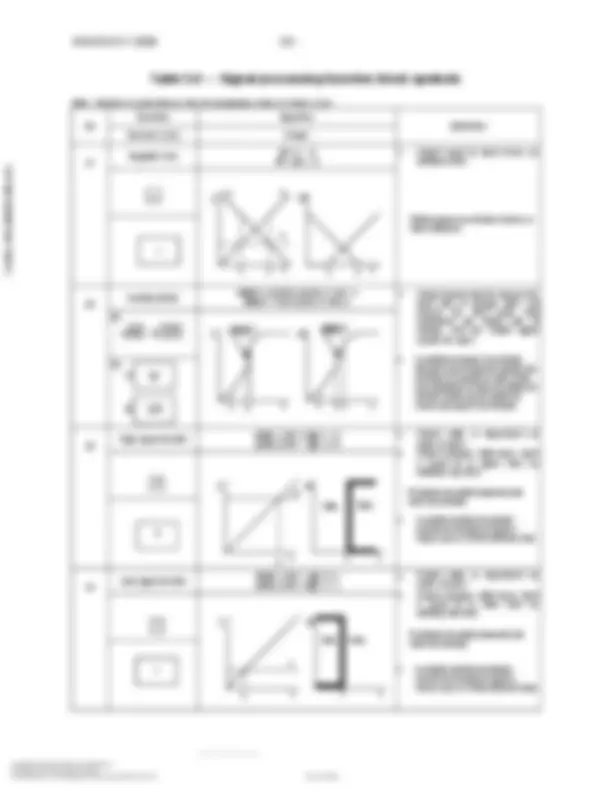
Note: Numbers in parentheses refer to explanatory notes in Clause 5.3.1. Shared display, Shared control (1) A B
No. Primary Choice or Basic Process Control System (2) Alternate Choice or Safety Instrumented System (3) Computer Systems and Software (4) Discrete (5) Location & accessibility (6) 1 Located in field. Not panel, cabinet, or console mounted. Visible at field location. Normally operator accessible. 2 Located in or on front of central or main panel or console. Visible on front of panel or on video display. Normally operator accessible at panel front or console. 3 Located in rear of central or main panel. Located in cabinet behind panel. Not visible on front of panel or on video display. Not normally operator accessible at panel or console. 4 Located in or on front of secondary or local panel or console. Visible on front of panel or on video display. Normally operator accessible at panel front or console. 5 Located in rear of secondary or local panel. Located in field cabinet. Not visible on front of panel or on video display. Not normally operator accessible at panel or console. Copyright International Society of Automation Provided by IHS under license with ISA
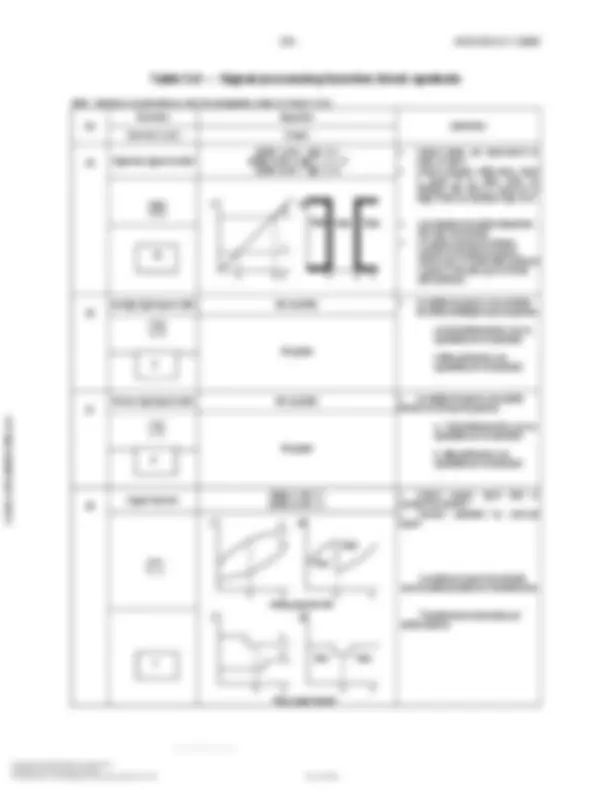
Note: Numbers in parentheses refer to explanatory notes in Clause 5.3.1. No Symbol Description 1 Signal processing function: Locate in upper right or left quadrant of symbols above. Attach to symbols above where affected signals are connected. Insert signal processing symbol from Table 5. Expand symbol by 50% increments for larger function symbols. 2 Panel-mounted patchboard plug-in point. Console matrix point. C-12 equals patchboard column and row respectively, as an example. 3 (7) (8) Generic interlock logic function. Undefined interlock logic function. 4 (7) (8) ‘AND’ interlock logic function. 5 (7) (8) ‘OR’ interlock logic function. 6 Instruments or functions sharing a common housing. It is not mandatory to show a common housing. Notes shall be used to identify instruments in common housings not using this symbol. 7 Pilot light. Circle shall be replaced with any symbol from column D in Table 5.1.1 if location and accessibility needs to be shown.
Copyright International Society of Automation Provided by IHS under license with ISA
Note: Numbers in parentheses refer to explanatory notes in Clause 5.3. Analysis AIR = Excess air H2O = Water O2 = Oxygen UV = Ultraviolet CO = Carbon monoxide H2S = Hydrogen sulfide OP = Opacity VIS = Visible light CO2 = Carbon dioxide HUM = Humidity ORP = Oxidation reduction VISC = Viscosity COL = Color IR = Infrared pH = Hydrogen ion = COMB = Combustibles LC = Liquid chromatograph REF = Refractometer = COND = Elec. conductivity MOIST = Moisture RI = Refractive index = DEN = Density MS = Mass spectrometer TC = Thermal conductivity = GC = Gas chromatograph NIR = Near infrared TDL = Tunable diode laser = Flow CFR = Constant flow regulator OP = Orifice plate PT = Pitot tube VENT = Venturi tube CONE = Cone OP-CT = Corner taps PV = Pitot venturi VOR = Vortex Shedding COR = Coriollis OP-CQ = Circle quadrant SNR = Sonar WDG = Wedge DOP = Doppler OP-E = Eccentric SON Sonic = DSON = Doppler sonic OP-FT = Flange taps TAR = Target FLN = Flow nozzle OP-MH = Multi-hole THER = Thermal = FLT = Flow tube OP-P = Pipe taps TTS = Transit time sonic = LAM = Laminar OP-VC = Vena contracta taps TUR = Turbine = MAG = Magnetic PD = Positive displacement US = Ultrasonic = Level CAP = Capacitance GWR = Guided wave radar NUC = Nuclear US = Ultrasonic d/p = Differential pressure LSR = Laser RAD = Radar = DI = Dielectric constant MAG = Magnetic RES = Resistance = DP = Differential pressure MS = Magnetostrictive SON = Sonic = Pressure ABS = Absolute MAN = Manometer VAC = Vacuum AVG = Average P-V = Pressure-vacuum = DRF = Draft SG = Strain gage = = Temperature BM = Bi-metallic RTD = Resistance temp detector TCK = Thermocouple type K TRAN = Transistor IR = Infrared TC = Thermocouple TCT = Thermocouple type T = RAD = Radiation TCE = Thermocouple type E THRM = Thermistor = RP = Radiation pyrometer TCJ = Thermocouple type J TMP = Thermopile = Miscellaneous Burner, Combustion Position Quantity Radiation FR = Flame rod CAP = Capacitance PE = Photoelectric = Alpha radiation IGN = Igniter EC = Eddy current TOG = Toggle = Beta radiation IR = Infrared IND = Inductive = = Gamma radiation TV = Television LAS = Laser = n = Neutron radiation UV = Ultraviolet MAG = Magnetic = = = MECH = Mechanical = = = OPT = Optical = = = RAD = Radar = = = = = = Speed Weight, Force ACC = Acceleration LC = Load cell = = EC = Eddy current SG = Strain gauge = = PROX = Proximity WS = Weigh scale = = VEL = Velocity = = = = = = = Copyright International Society of Automation Provided by IHS under license with ISA
Note: Numbers in parentheses refer to explanatory notes in Clause 5.3.2. No Symbol (4) Description Analysis
Conductivity, moisture, etc. Single element sensing probe. Analysis
pH, ORP, etc. Dual element sensing probe. Analysis
Fiberoptic sensing probe. Burner
Ultraviolet flame detector. Television flame monitor. Burner
Flame rod flame detector. Flow
Generic orifice plate. Restriction orifice. Flow
Orifice plate in quick-change fitting. Flow
Concentric circle orifice plate. Restriction orifice. Flow
Eccentric circle orifice plate. Flow
Circle quadrant orifice plate. Flow
Multi-hole orifice plate Flow
Generic venturi tube, flow nozzle, or flow tube. Notation from Table 5.2.2 required at (*) if used for more than one type. Flow
Venturi tube. Flow
Flow nozzle. Flow
Flow tube.
Copyright International Society of Automation Provided by IHS under license with ISA
Note: Numbers in parentheses refer to explanatory notes in Clause 5.3.2. No Symbol (4) Description Flow
Open channel flume. Level
Displacer internally mounted in vessel. Level
Ball float internally mounted in vessel. May be installed through top of vessel. Level
Radiation, single point. Sonic. Level
Radiation, multi-point or continuous. Level
Dip tube or other primary element and stilling well. May be installed through side of vessel. May be installed without stilling well. Level
Float with guide wires. Location of readout should be noted, at grade, at top, or accessible from a ladder. Guide wires may be omitted. Level
Insert probe. May be through top of vessel. Level
Radar. Pressure
Strain gage or other electronic type sensor. Notation (*) from Table 5.2.2 should be used to identify type of element. Connection symbols 6, 7, 8, or 9 in Table 5.3.1 are used if connection type is to be shown. Bubble may be omitted if connected to another instrument.
Copyright International Society of Automation Provided by IHS under license with ISA
Note: Numbers in parentheses refer to explanatory notes in Clause 5.3.2. No Symbol (4) Description Temperature
Generic element without thermowell. Notation (*) should be used to identify type of element, see Table 5.2.2. Connection symbols 6, 7, 8, or 9 in Table 5.3.1 are used if connection type is to be shown. Bubble may be omitted if connected to another instrument.
Note: Numbers in parentheses refer to explanatory notes in Clause 5.3.2. No Symbol (4) Description Flow
Sight glass. Level
Gage integrally mounted on vessel. Sight glass. Level
Gage glass externally mounted on vessel or standpipe. Multiple gages may be shown as one bubble or one bubble for each section. Use connection 6, 7, 8, or 9 in Table 5.3.1 if connection type is to be shown. Pressure
Pressure gage. Use connection 6, 7, 8, or 9 in Table 5.3.1 if connection type is to be shown. Temperature
Thermometer. Use connection 6, 7, 8, or 9 in Table 5.3.1 if connection type is to be shown.
Copyright International Society of Automation Provided by IHS under license with ISA
Note: Numbers in parentheses refer to explanatory notes in Clause 5.3.3. No Symbol Application 1 Instrument connections to process and equipment. Process impulse lines. Analyzer sample lines. 2 Heat [cool] traced impulse or sample line from process. Type of tracing indicated by: [ET] electrical, [ST] steam, [CW] chilled water, etc. 3 Generic instrument connection to process line. Generic instrument connection to equipment. 4 Heat [cool] traced generic instrument impulse line. Process line or equipment may or may not be traced. 5 Heat [cool] traced instrument. Instrument impulse line may or may not be traced. 6 Flanged instrument connection to process line. Flanged instrument connection to equipment. 7 Threaded instrument connection to process line. Threaded instrument connection to equipment. 8 Socket welded instrument connection to process line. Socket welded instrument connection to equipment. 9 Welded instrument connection to process line. Welded instrument connection to equipment.
Copyright International Society of Automation Provided by IHS under license with ISA
Note: Numbers in parentheses refer to explanatory notes in Clause 5.3.3. No Symbol Application 1 (1) IA may be replaced by PA [plant air], NS [nitrogen}, or GS [any gas supply]. Indicate supply pressure as required, e.g., PA-70 kPa, NS-150 psig, etc. 2 (1) Instrument electric power supply. Indicate voltage and type as required, e.g. ES-220 Vac. ES may be replaced by 24 Vdc, 120 Vac, etc. 3 (1) Instrument hydraulic power supply. Indicate pressure as required, e.g., HS-70 psig. 4 (2) Undefined signal. Use for Process Flow Diagrams. Use for discussions or diagrams where type of signal is not of concern. 5 (2) Pneumatic signal, continuously variable or binary. 6 (2) (^) Electronic or electrical continuously variable or binary signal. Functional diagram binary signal. 7 (2) (^) Functional diagram continuously variable signal. Electrical schematic ladder diagram signal and power rails. 8 (2) (^) Hydraulic signal. 9 (2) (^) Filled thermal element capillary tube. Filled sensing line between pressure seal and instrument. 10 (2) Guided electromagnetic signal. Guided sonic signal. Fiber optic cable. 11 (3) Unguided electromagnetic signals, light, radiation, radio, sound, wireless, etc. Wireless instrumentation signal. Wireless communication link. 12 (4) Communication link and system bus, between devices and functions of a shared display, shared control system. DCS, PLC, or PC communication link and system bus. 13 (5) Communication link or bus connecting two or more independent microprocessor or computer- based systems. DCS-to-DCS, DCS-to-PLC, PLC-to-PC, DCS-to-Fieldbus, etc. connections. 14 (6) Communication link and system bus, between devices and functions of a fieldbus system. Link from and to “intelligent” devices. 15 (7) (^) Communication link between a device and a remote calibration adjustment device or system. Link from and to “smart” devices.
a) b) Copyright International Society of Automation Provided by IHS under license with ISA
Note: Numbers in parentheses refer to explanatory notes in Clause 5.3.4. No Symbol Description 1 (1) (2) (^) Generic two-way valve. Straight globe valve. Gate valve. 2 (2) (3) Generic two-way angle valve. Angle globe valve. Safety angle valve. 3 (2) Generic three-way valve. Three-way globe valve. Arrow indicates failure or unactuated flow path. 4 (2) Generic four-way valve. Four-way four-ported plug or ball valve. Arrows indicates failure or unactuated flow paths. 5 (2) (^) Butterfly valve. 6 (2) (^) Ball valve. 7 (2) Plug valve 8 (2) Eccentric rotary disc valve. 9 (1) (2) (^) Diaphragm valve. 10 (2) (^) Pinch valve. 11 (2) (^) Bellows sealed valve. 12 (2) Generic damper. Generic louver. 13 (2) Parallel blade damper. Parallel blade louver. 14 (2) (^) Opposed blade damper. Opposed blade louver.
Copyright International Society of Automation Provided by IHS under license with ISA
Note: Numbers in parentheses refer to explanatory notes in Clause 5.3.4. No Symbol Description 15 (4) (^) Two-way on-off solenoid valve. 16 (4) (^) Angle on-off solenoid valve. 17 (4) Three-way on-off solenoid valve. Arrow indicates de-energized flow path. 18 (4) Four-way plug or ball on-off solenoid valve. Arrows indicates de-energized flow paths. 19 (4) (^) Four-way five-ported on-off solenoid valve. Arrows indicates de-energized flow paths. 20 (5) (^) Permanent magnet variable speed coupling. 21 (6) (^) Electric motor. Copyright International Society of Automation Provided by IHS under license with ISA