














Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Prokaryotes are bacteria. Unicellular with a cell wall. Cell wall can be stained. Why are these differences in cell wall structure so important?
Typology: Lecture notes
1 / 21

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!














Prokaryote Cell vs Eukaryote Cell
How are these alike? How are they different?
Karen Storey; Kernersville Middle School September 12, 2014 (^) Cell Diagram: Mariana Ruiz, pub domain
The Cellular Level of Organization
Living things are constructed of cells.
Living things may be unicellular ormulticellular.
Cell structure is diverse but all cells share common characteristics.
Cells are small so they can exchange materials with their surroundings.
Surface area relative to the volume decreases as size of cell increases.
TEACHER HINT! KNOW THIS…. __________CELL THEORY_______ states:
Why are these differences in cell wall structure so important?
Images: Sources unknown
We use the color of the stain to determine what type of antibiotic to use to eliminate the disease they cause.
Gram-positive (purple) Gram-negative (red)
Prokaryotes - Cell Wall
Images: PHIL Public Health Image Library
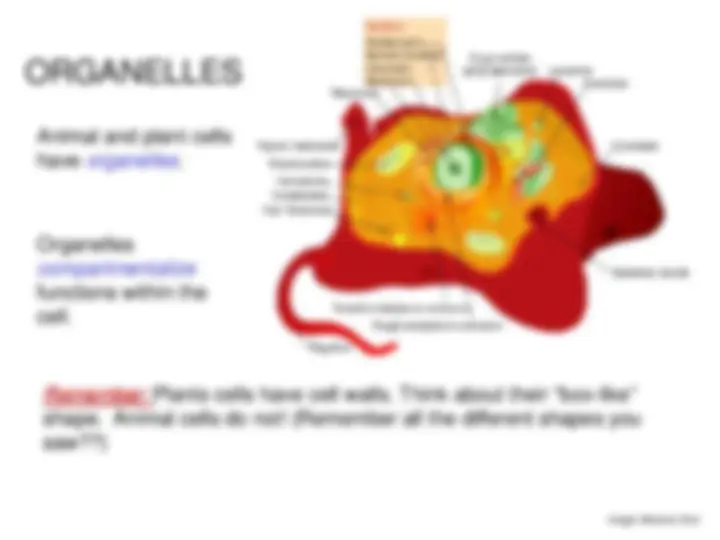
Remember: Plants cells have cell walls. Think about their “box-like” shape. Animal cells do not! (Remember all the different shapes you saw??)
Animal and plant cells have organelles.
Organelles compartmentalize functions within the cell.
Image: Mariana Ruiz
Now let’s talk about additional structures found in PLANT Cells !!
So there are really two basic types of cells
______Prokaryote : (bacteria)_________ Almost always single-celled
Reproduce by binary fission (another copy by dividing). No cell nucleus or any other membrane-bound organelles. DNAtravels openly around the cell.
_______Eukaryote : (plant or animal)_______ Most organisms that we can see, such as trees, grass, worms,flies, mice, humans, mushrooms and yeast are eukaryotes.
Can either be single-celled or multi-celled. Can reproduce in one of several ways (Ex. meiosis, mitosis). Have cell nucleus within containing its DNA. Nucleus most evident distinction between these cell types.
Images: Mariana Ruiz
Plant Cell (Eukaryote)
Image: Mariana Ruiz
So how are Eukaryotic (Protist, Animal, & Plant) and Prokaryotic Cells (Bacteria) alike and how are they different?
Image:k12station.blogspot.com/2006_08_01_archive.html