























Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Neurons are cells that transfer electrical signals throughout the body. Parts of a neuron include: •Dendrites. •Cell body. •Nucleus. •Axon. •Myelin Sheath.
Typology: Lecture notes
1 / 30

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!























The nervous system provides for coordination of all body functions — both voluntary and involuntary. It is also the system that houses intellect, memory, and emotion. The nervous system has two major divisions: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system.
The functional unit of the nervous system is a specialized cell called a neuron. Hundreds of billions of neurons make up a human nervous system and permit the relay of electrochemical messages throughout the body.
Cell Body Nucleus Dendrites Axon Schwan Cells Nodes of Ranvier Terminal Branches Synaptic Knobs
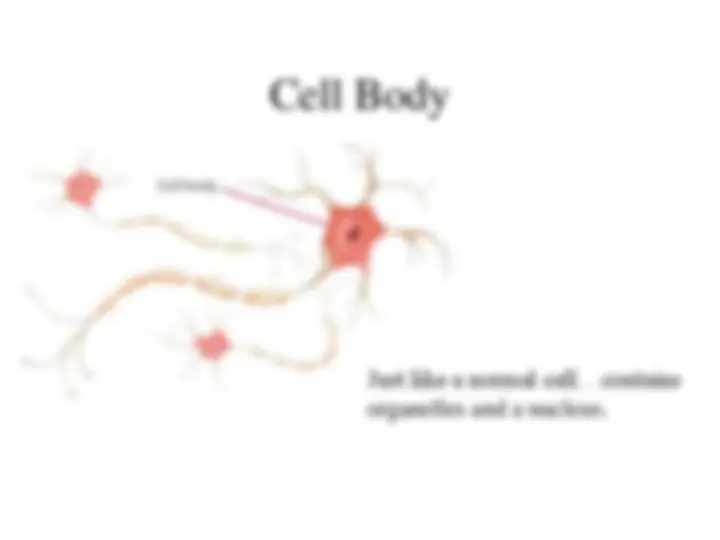
Just like a normal cell…contains organelles and a nucleus.
Long thin fiber that carries the impulse away from the cell body to other neurons or effector organs
Cells that surround the axon, often they secrete a fatty substance called Myelin
The axon branches out into finger like projections called terminal branches. The ends of these branches are called Synaptic Knobs
The gap between the terminal branch of one neuron and the dendrites of another.
Resting potential is the electrical potential across the cell membrane of a nerve cell or muscle cell when the cell is not active. When a neuron is at rest the inside of the nerve is negative while the outside is positive
Action potential is a sudden change in the polarity of the membrane of a neuron, facilitates the transmission of electrical impulses. A stimulus causes Sodium to rush into the cell causing the polarity to change
After the action potential has passed the Sodium and Potassium ions need to be brought back to their respective sides of the axon membrane. The Sodium Potassium pump uses active transport to push each ion against its concentration gradient to restore the original polarity.
The Action potential moves down the axon to the terminal branches. At the terminal branches vesicles containing neurotransmitters are stimulated.
The neurotransmitter is released. The neurotransmitter crosses the synapse
The dendrites of the next neuron contain receptors that will bind with the neurotransmitter.