


Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
This is an introductory course in Data Communication and Computer Networks. The course is designed with objectives: Provide solid foundation in the field of data communication and computer networks, give practical experience on networks and networking devices, introduce the cutting edge technologies. This is solution to quiz with main points: Data, Communication, Analog, Frequency, Sampling, Rate, Signals, Multiplexed, Transmitted, Channel
Typology: Exercises
1 / 3

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!



On special offer
EEE314: Data Communication And Computer Networks Program: BS Electrical (TE/CE) Engineering Semester: 6th Date: 25 th April, 20 09 Instructions for attempting paper Mobile phones and digital diaries are not allowed in the examination hall. Answer all questions.
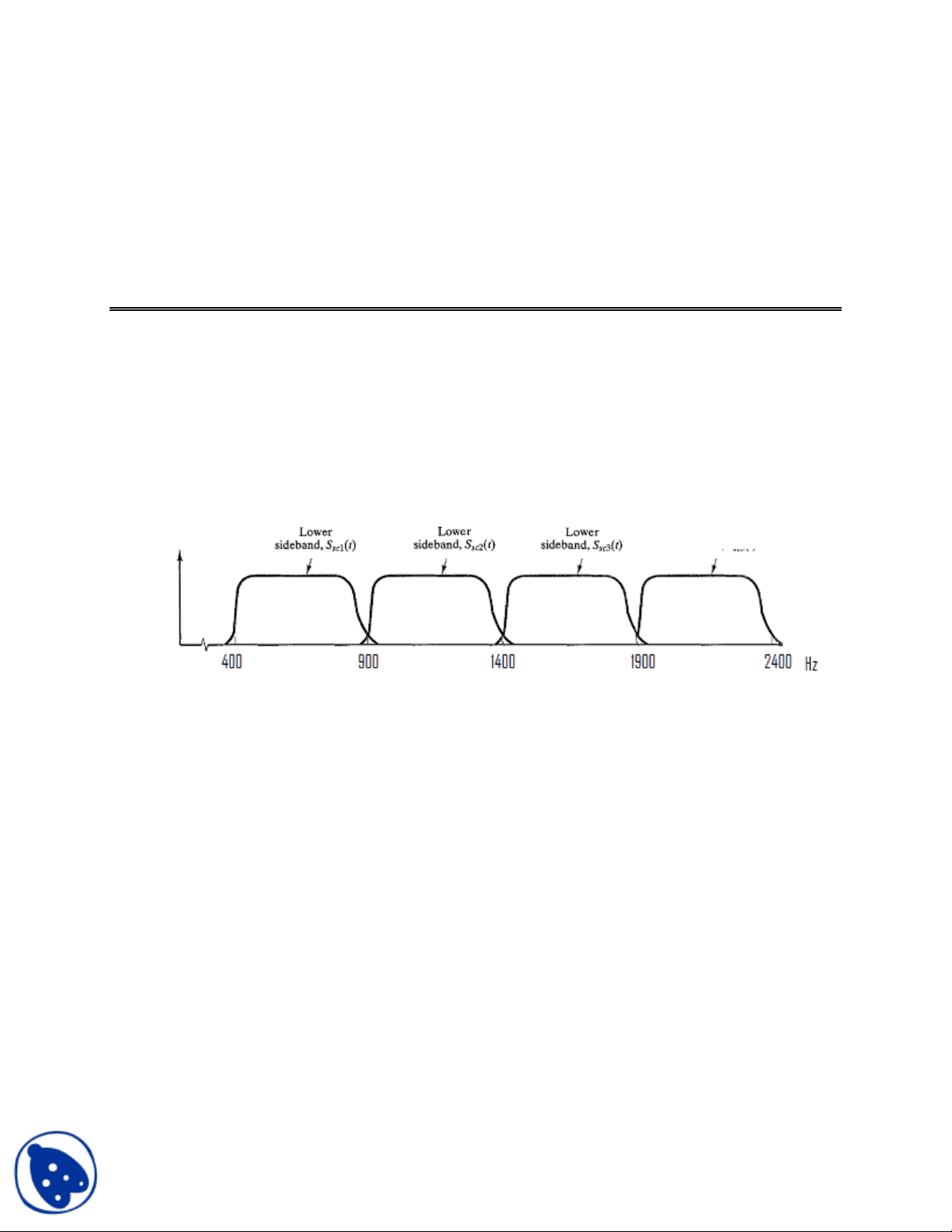
Q No.1. [15 Marks] The information in four analog signals is to be multiplexed and transmitted over a telephone channel that has a 400 to 3100-Hz bandpass. Each of the analog baseband signals is bandlimited to 500 Hz. Design a communication system (block diagram) that will allow the transmission of these four sources over the telephone channel using a) Frequency-division multiplexing with SSB (single sideband) subcarriers. Refer to fig 1.a
b) Time-division multiplexing using 6-bit PCM. What data rate must be supported in the available bandwidth. (5) BW = 3100 – 400 = 2700 Hz For 500 Hz bandlimited signals the sampling rate would be = 500 x 2 Data Rate for Each Signal = 1000 x 6 = 6000 bps Net Data Rate for 4 sources = 6000 x 4 = 24 kbps
c) Why parallel transmission is not suitable for long distance communication? (2)
d) Why NRZ signaling is used in asynchronous communication? (2) In asynchronous communication synchronization is achieved at every byte by start and end bit so the most simple encoding scheme is used. There is no need to bear the overhead of providing synchronization through encoding scheme. Synchronization through encoding scheme comes at the cost of increased signal bandwidth e) What is Dense-WDM? (1) No fixed definition, carriers are closely spaced than WDM
2nd Sessional
Q. No. 2. [15 Marrks] a) Find the FCS for given data and predetermined divisor represented in polynomial form? (7) D = 1010101101 P(X) = X^5 + X^4 + X^2 + 1
b) Calculate the Hamming pairwise distance among the following code words? (4) i) 000000, 010101, 101010, 110110
000000 010101 = 3 000000 101010 = 3 000000 110110 = 4 010101 101010 = 6 010101 110110 = 3 101010 110110 = 3
c) In CRC, show the relationship between the following entities (size means the number of bits): (4) i. The size of the dataword and the size of the codeword (Sizecodeword = Sizedataword + SizeFCS) ii. The size of the divisor and the remainder (Sizeremainder = Sizedivisor -1) ii. The degree of the polynomial generator and the size of the divisor Degree = Sizedivisor – 1 iii. The degree of the polynomial generator and the size of the remainder
Degree = Sizeremainder
Q. No. 3. [15 Marks] a) Consider the use of 500-bit frames on a 1.5-Mbps satellite channel with a 250-ms delay. What is the maximum link utilization for (9) i. Stop-and-wait flow control? ii. Continuous flow control with a window size of 63? iii. Continuous flow control with a window size of 127? b) What are the applications of infrared (IRD) (2) Remote control Short range communication e.g. mobile to mobile c) Find all the orthogonal codes for 8 chip CDMA? (4)
Q. No. 4. [15 Marks] a) Determine the Huffman code? Assume capital and small letter is same. (5) “my name is <your_first_name>” b) Use RLE to compress the data. Make sure that for any substitution the overhead does not exceed the compression achieved. Assume integer takes 2 bytes and special character 1 byte. (3) ABBCDDDDEEEEEGGG