









































































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
This lecture is part of lecture series on Data Communication Systems. It was delivered by Prof. Prajin Ahuja at Birla Institute of Technology and Science. Its main points are: Corrupted, Application, Detected, Length, Extra, Redundant, Convolution, Coding, Redundant, Hamming
Typology: Slides
1 / 92

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!





















































































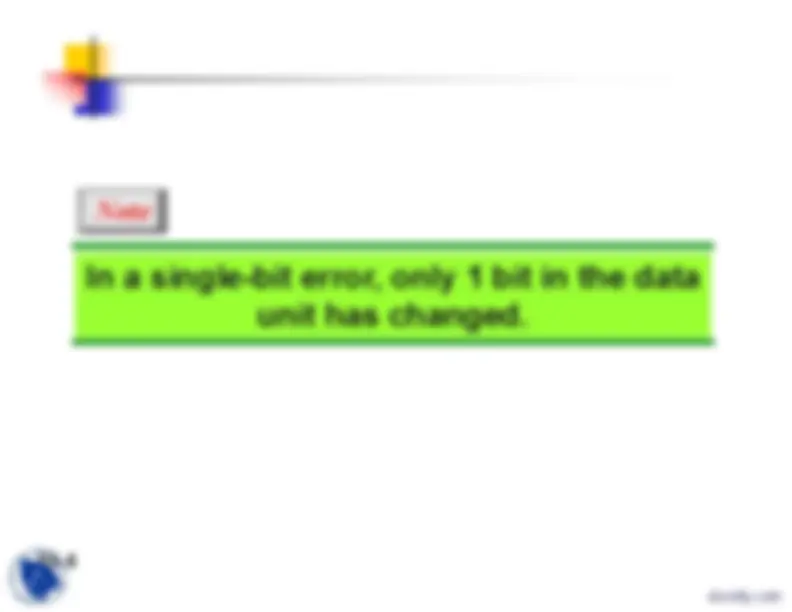
Note
Let us first discuss some issues related, directly orindirectly, to error detection and correction. Topics discussed in this section: Types of ErrorsRedundancyDetection Versus CorrectionForward Error Correction Versus RetransmissionCodingModular Arithmetic
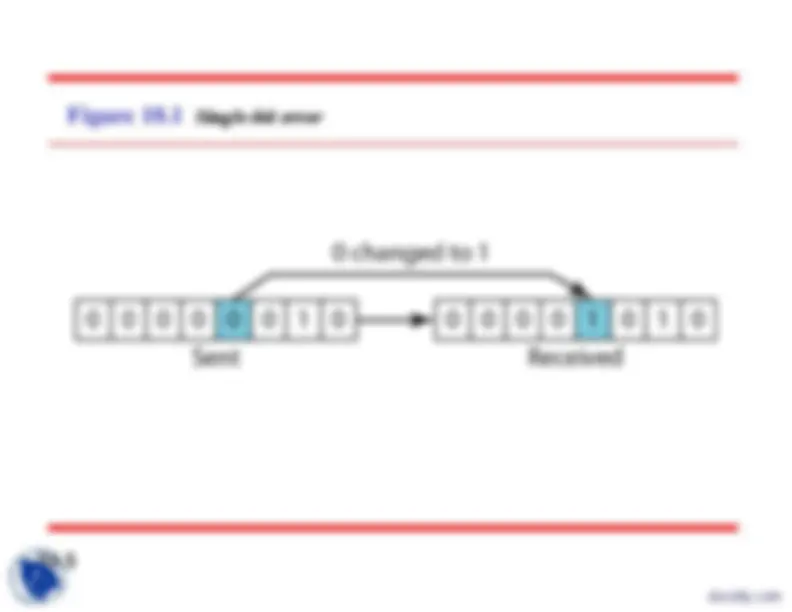
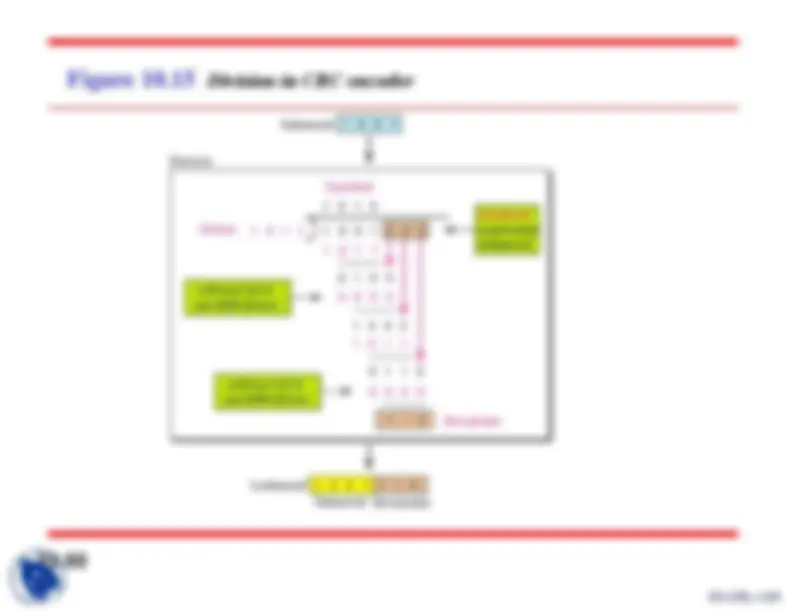
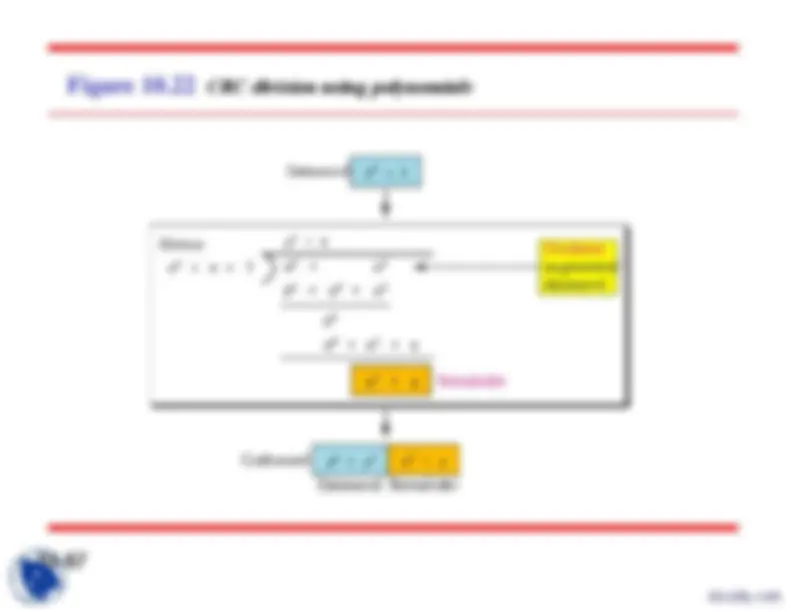
Figure 10.
Single-bit error
Note
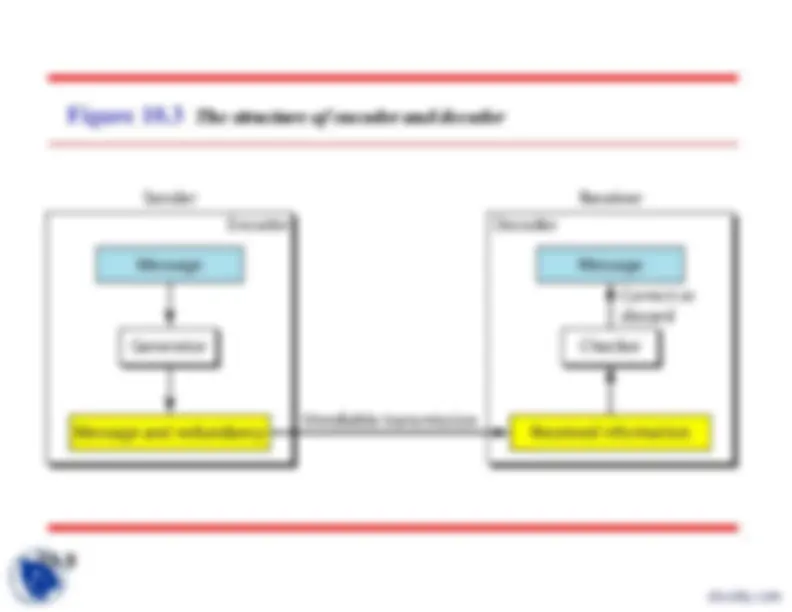
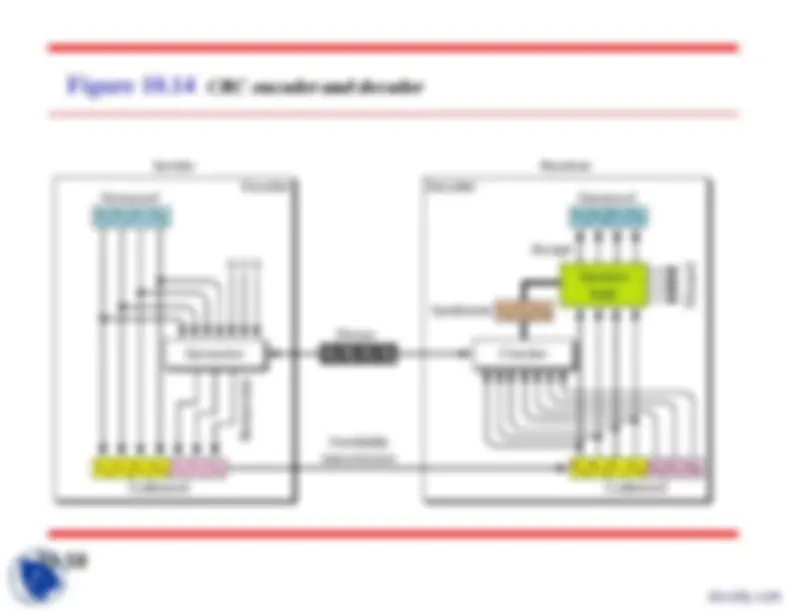
Figure 10.
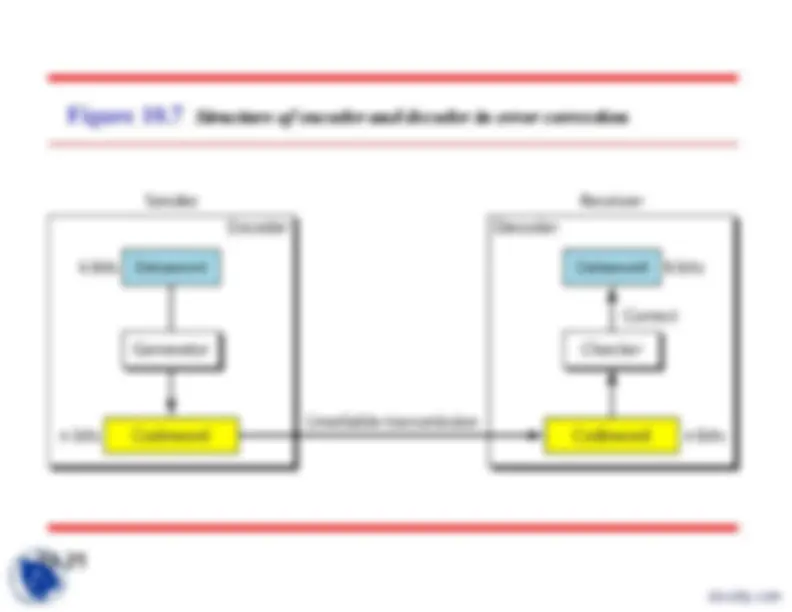
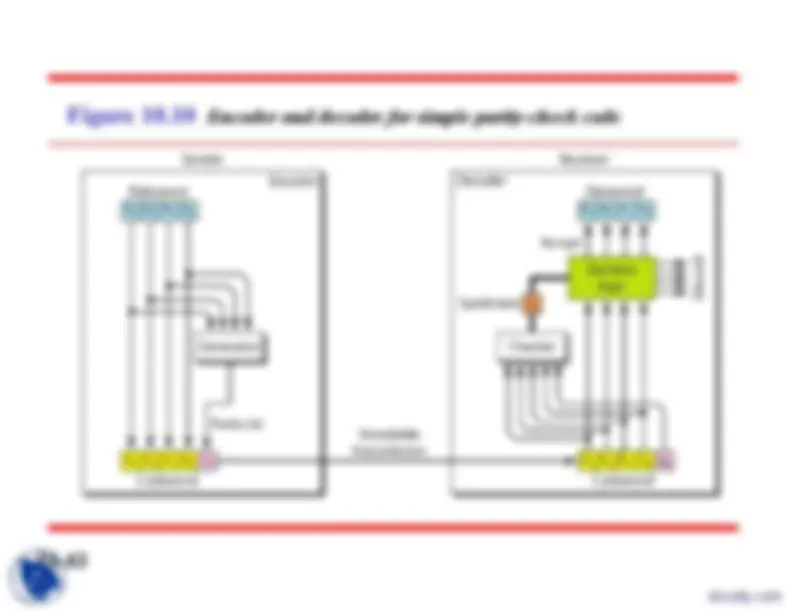
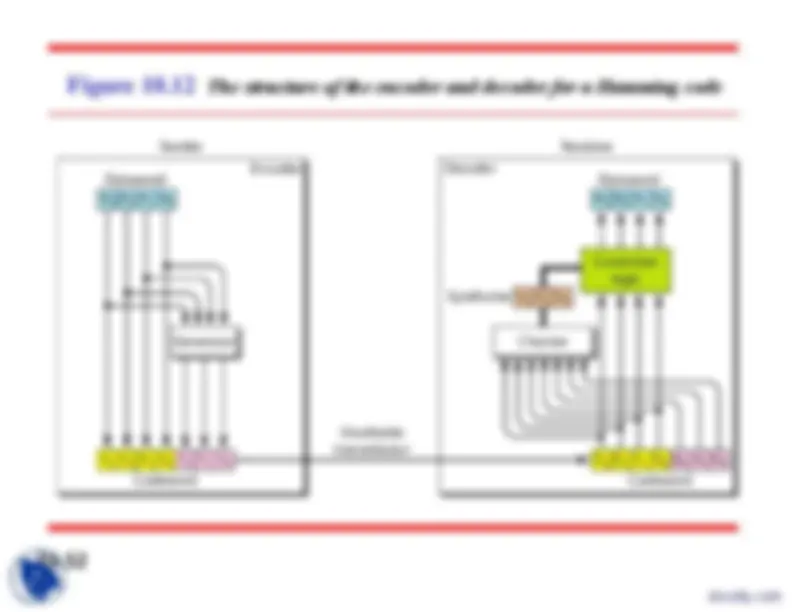
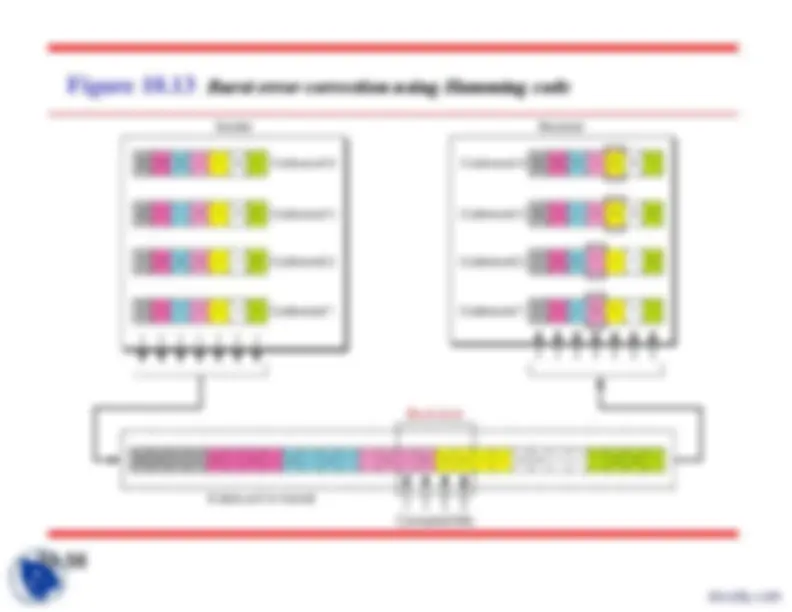
The structure of encoder and decoder
Note
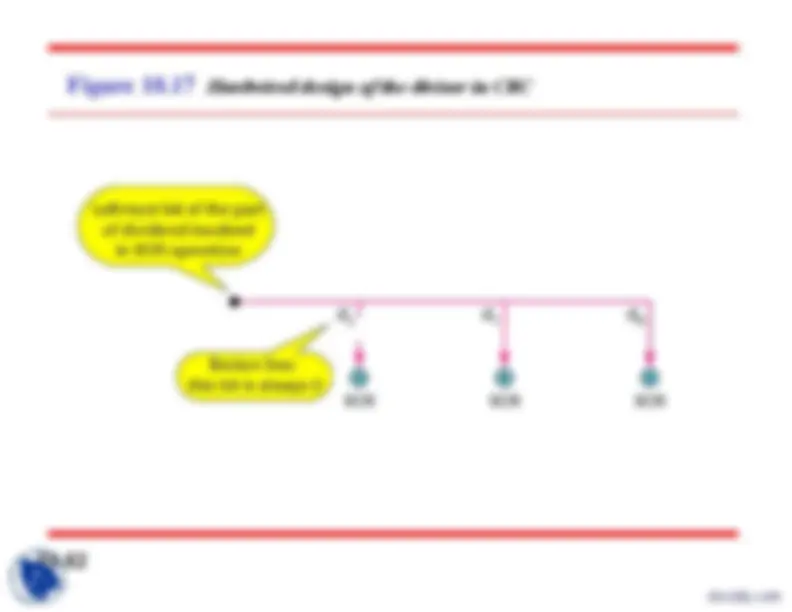
Figure 10.
XORing of two single bits or two words
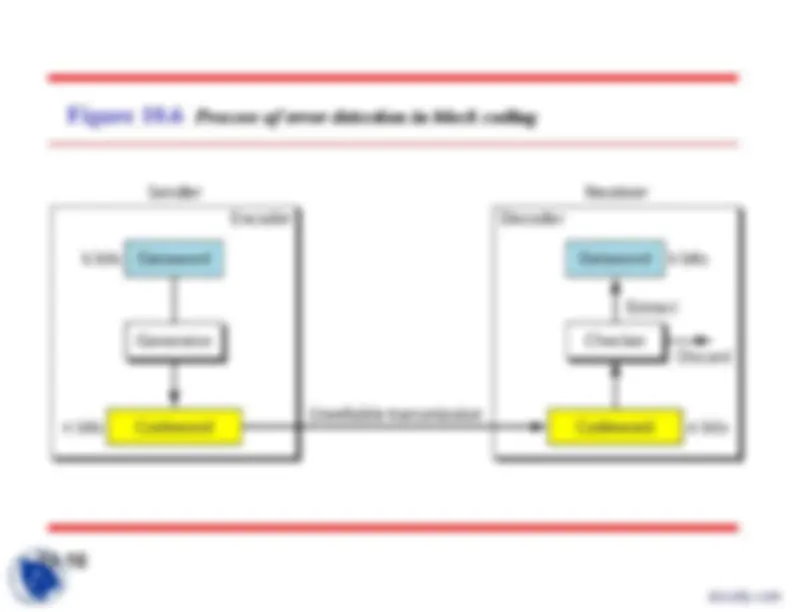
Figure 10.
Datawords and codewords in block coding
The 4B/5B block coding discussed in Chapter 4 is a goodexample of this type of coding. In this coding scheme,k = 4 and n = 5. As we saw, we have 2
k^
= 16 datawords
and
n^
codewords.
We
saw
that
out
of
codewords are used for message transfer and the rest areeither used for other purposes or unused.
Let us assume that k = 2 and n = 3. Table 10.1 shows the
list of datawords and codewords. Later, we will seehow to derive a codeword from a dataword. Assume the sender encodes the dataword 01 as 011 andsends it to the receiver. Consider the following cases:1. The receiver receives 011. It is a valid codeword. The
receiver extracts the dataword 01 from it.
111 is received. This is not a valid codeword and isdiscarded.
000 is received. This is a valid codeword. The receiverincorrectly extracts the dataword 00. Two corruptedbits have made the error undetectable.
Note
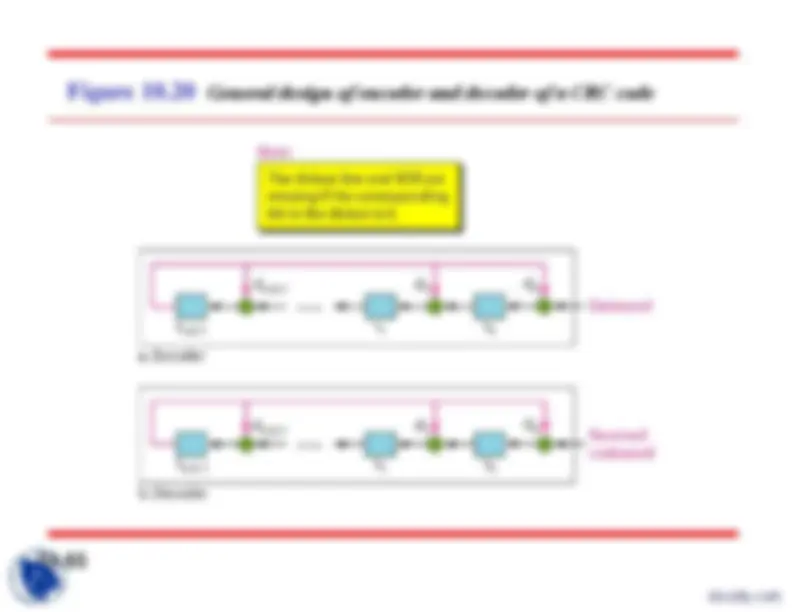
Figure 10.
Structure of encoder and decoder in error correction